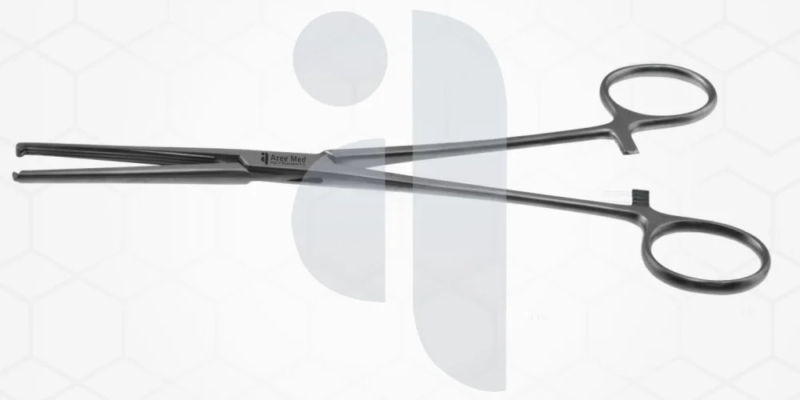
Bowel clamps are specialized surgical instruments used in gastrointestinal procedures to control and manage the intestines during surgery. These bowel clamps are designed to temporarily occlude sections of the bowel, preventing the flow of contents while allowing surgeons to perform delicate tasks such as resections, anastomoses, or repairs. Their precise functionality and careful design make them indispensable tools in abdominal surgeries, ensuring a controlled and safe surgical environment.
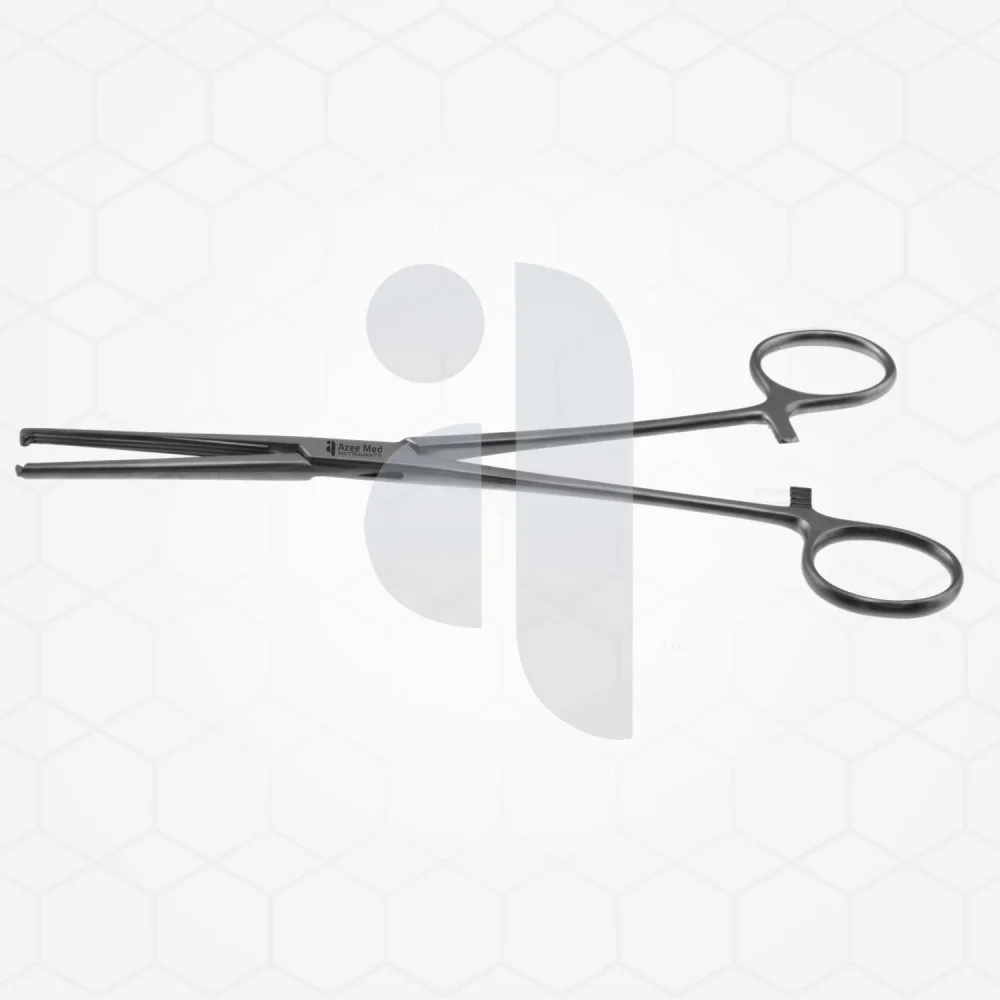
The Design and Functionality of Bowel Clamps
Bowel clamps are typically long, slender instruments with curved or straight jaws that are carefully designed to grasp intestinal tissue without causing excessive trauma. The jaws are often coated with atraumatic serrations or smooth surfaces to provide a secure hold while minimizing damage to the delicate bowel walls. This design helps prevent complications such as perforations, ischemia, or excessive pressure injuries, which could lead to post-operative complications.
Many bowel clamps are made from high-quality stainless steel, ensuring durability and resistance to corrosion. Some models feature ratcheted handles to maintain consistent pressure, allowing surgeons to keep the clamp in place without needing continuous manual force. The gentle yet firm grip of these instruments enables precise manipulation of the intestines, which is crucial for successful surgical outcomes.
Importance of Bowel Clamps in Surgical Procedures
Bowel clamps play a crucial role in various gastrointestinal surgeries, particularly in procedures involving the resection or repair of the intestines. When a section of the bowel needs to be removed due to conditions such as cancer, obstruction, or perforation, these clamps help isolate the affected area, preventing contamination and ensuring a controlled surgical field. By temporarily occluding the bowel, they prevent leakage of intestinal contents, reducing the risk of infections such as peritonitis.
In anastomosis procedures, where two segments of the bowel are joined together, the use of clamps helps stabilize the tissues, allowing surgeons to suture or staple with precision. Without proper occlusion, the movement of intestinal contents could interfere with the delicate suturing process, increasing the likelihood of leaks or incomplete closures.
Types of Bowel Clamps and Their Applications
There are several types of bowel clamps, each designed for specific surgical needs. Some of the most commonly used include Doyen, Kocher, and Allen clamps. Doyen bowel clamps are known for their long, flexible jaws with smooth surfaces, making them ideal for occluding the bowel without crushing tissue. Kocher clamps, on the other hand, have toothed jaws and are often used for grasping tougher tissues when a firmer hold is required. Allen clamps provide a balance between secure occlusion and gentle handling, making them suitable for a variety of gastrointestinal procedures.
Surgeons select the appropriate clamp based on the specific requirements of the procedure, ensuring that bowel tissues are handled with care to minimize post-operative complications. The choice of instrument depends on factors such as tissue fragility, surgical approach, and the need for temporary or extended occlusion.
Conclusion
Bowel clamps are vital instruments in gastrointestinal surgery, providing surgeons with the necessary control to perform delicate procedures safely. Their ability to temporarily occlude sections of the bowel while preserving tissue integrity makes them invaluable in ensuring successful outcomes. By preventing contamination, stabilizing tissues, and allowing precise surgical interventions, these clamps contribute to improved patient recovery and reduced risks of complications. As a fundamental part of surgical toolkits, bowel clamps continue to play a critical role in modern abdominal surgery.