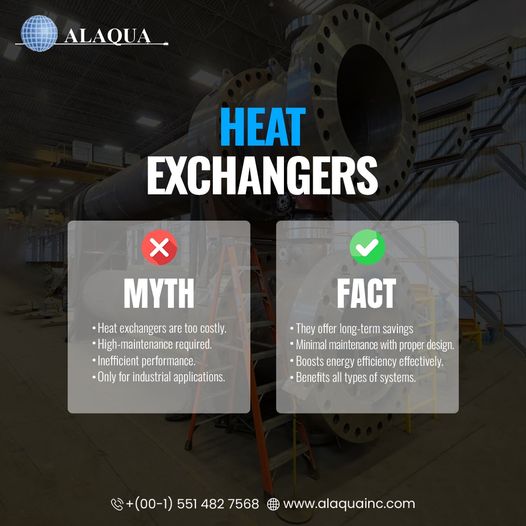
Heat exchangers are vital components in many industrial applications, including power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. They facilitate the transfer of heat between two or more fluids, which can significantly impact energy efficiency and overall system performance. However, like any mechanical equipment, heat exchangers can encounter issues that affect their functionality. Understanding these common problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining efficiency and extending the lifespan of heat exchangers.
In this blog, we’ll explore the most frequent issues associated with heat exchangers and provide practical solutions to resolve them.
The Most Common Problems With Heat Exchangers
Frequent issues with the heat exchangers include:-
1. Fouling
Fouling refers to the accumulation of unwanted materials on the heat transfer surfaces, reducing heat transfer efficiency and flow rates. Further, it can occur due to the deposition of scale, biological growth, corrosion products, or particulate matter.
Causes of Fouling:
-
Chemical Reactions: Interactions between fluids can lead to precipitation.
-
Temperature Variations: High temperatures can promote scaling and deposition.
-
Fluid Velocity: Low flow velocities can lead to sedimentation.
Solutions:
-
Regular Cleaning: Implement regular cleaning schedules using chemical cleaning agents or high-pressure water jets.
-
Increased Flow Velocity: Design modifications to enhance flow rates can help minimize fouling.
-
Filtration: Install filters to remove particulates from the fluids before they enter the heat exchanger.
-
Use of Anti-fouling Coatings: Consider applying special coatings that reduce fouling tendencies.
2. Corrosion
Corrosion is a slow process of material degradation caused by chemical reactions between the material and its surrounding environment. This deterioration can result in structural weaknesses, leaks, and diminished efficiency in equipment, ultimately leading to increased maintenance costs and operational failures.
Causes of Corrosion:
-
Chemical Composition of Fluids: The presence of corrosive substances, such as acids or salts, can accelerate corrosion.
-
Temperature and Pressure: Elevated conditions can enhance corrosion rates.
-
Dissimilar Metals: Contact between different metals can lead to galvanic corrosion.
Solutions:
-
Material Selection: Use corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or titanium for heat exchangers in corrosive environments.
-
Protective Coatings: Apply protective coatings to the surfaces to minimize exposure to corrosive agents.
-
Cathodic Protection: Implement cathodic protection systems to prevent galvanic corrosion.
-
Regular Inspection: Schedule routine inspections to identify and address corrosion early with the heat exchanger maker.
3. Leakage
Leakage in a heat exchanger occurs when fluids escape from the system, potentially causing operational disruptions, reduced efficiency, equipment damage, and heightened safety risks. Moreover, it can lead to environmental hazards, regulatory violations, and costly repairs or downtime.
Causes of Leakage:
-
Worn Seals or Gaskets: Over time, seals can degrade and fail.
-
Fatigue or Cracks: Mechanical fatigue from thermal cycling or pressure changes can cause cracks.
-
Improper Installation: Poor installation practices can lead to misalignments and leaks.
Solutions:
-
Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on seals, gaskets, and connections to identify signs of wear.
-
Proper Installation Techniques: Ensure correct installation practices are followed to prevent misalignments.
-
Use High-Quality Seals: Invest in high-quality seals and gaskets designed for specific operating conditions.
-
Pressure Testing: Implement pressure testing protocols to detect leaks before they cause significant damage.
4. Temperature Imbalances
Temperature imbalances in a heat exchanger arise when the outlet temperature of one fluid significantly deviates from its expected range. Therefore, signaling potential inefficiency or malfunction. Therefore, this can result in reduced heat transfer performance, increased energy consumption, and operational instability.
Causes of Temperature Imbalances:
-
Insufficient Heat Transfer Surface Area: An undersized heat exchanger may not provide adequate heat transfer.
-
Fouling: Accumulation of deposits can hinder effective heat transfer.
-
Flow Rate Variations: Changes in flow rates can affect the heat exchange process.
Solutions:
-
Evaluate Heat Exchanger Size: Conduct a thorough evaluation to ensure the heat exchanger is properly sized for the application.
-
Monitor Flow Rates: Implement flow rate monitoring systems to maintain optimal flow conditions.
-
Inspect for Fouling: Regularly inspect and clean the heat exchanger to minimize fouling effects.
5. Thermal Shock
Thermal shock in a heat exchanger happens when it undergoes abrupt temperature changes, causing uneven expansion and contraction of materials. Further, this rapid stress can lead to cracks, leaks, or even structural failure, reducing the equipment’s lifespan and operational efficiency.
Causes of Thermal Shock:
-
Rapid Changes in Fluid Temperature: Sudden changes in the inlet temperature of either fluid can induce thermal stress.
-
Inadequate Design: Poor design can fail to accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of materials.
Solutions:
-
Controlled Start-Up Procedures: Implement controlled start-up and shutdown procedures to avoid rapid temperature changes.
-
Thermal Expansion Design: Consider using materials and designs that accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
-
Use of Expansion Joints: Incorporate expansion joints to relieve stress in the system.
6. Pressure Drop Issues
A pressure drop in a heat exchanger evaporator occurs when fluid pressure decreases as it flows through the system. This can reduce overall efficiency, increase energy consumption, and cause operational issues, such as reduced heat transfer, flow disruptions, or equipment strain.
Causes of Pressure Drop Issues:
-
Fouling: As mentioned earlier, fouling can increase resistance to fluid flow.
-
Blockages: Any blockages in the flow paths can lead to significant pressure drops.
-
Incorrect Design: An improperly designed heat exchanger may not handle the intended flow rates efficiently.
Solutions:
-
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning: Ensure regular maintenance to prevent fouling and blockages.
-
Flow Path Optimization: Evaluate the design to minimize bends and obstructions in the flow path.
-
Install Pressure Monitoring: Utilize pressure gauges to monitor pressure drop trends and address issues promptly.
7. Noise and Vibration
Noise and vibration in heat exchangers during operation can signal underlying mechanical problems, such as loose components, flow disturbances, or wear and tear. Moreover, if left unaddressed, these issues can lead to reduced efficiency, equipment damage, or system failure.
Causes of Noise and Vibration:
-
Flow Turbulence: Turbulent flow can generate noise and vibrations.
-
Loose Components: Worn or loose components can lead to increased vibration.
-
Mechanical Imbalance: Imbalance in rotating equipment associated with the heat exchanger can cause vibrations.
Solutions:
-
Damping Mechanisms: Incorporate damping mechanisms or mounts to reduce vibrations.
-
Regular Inspection: Regularly check for loose components and tighten or replace them as necessary.
-
Flow Optimization: Analyze flow patterns to minimize turbulence and associated noise.
Concluding
Maintaining the efficiency and reliability of heat exchangers is essential for optimal operation in various industrial applications. By understanding common issues such as fouling, corrosion, leakage, temperature imbalances, thermal shock, pressure drop problems, and noise/vibration, you can implement effective solutions to mitigate these challenges.
Regular maintenance, inspections, and proper design considerations are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of heat exchangers. By addressing these common problems proactively, you can enhance energy efficiency, reduce downtime, and achieve overall operational excellence.
AlaqauaInc., a leading supplier of heat exchangers, collaborates closely with heat exchanger maker in usa to deliver high-quality, efficient systems. This partnership ensures tailored solutions, superior product performance, and continuous innovation to meet the evolving needs of various industries.