In the world of viral infections, two names frequently come up: herpes zoster and herpes simplex. While they share similarities as members of the herpesvirus family, they are fundamentally different in terms of their causes, symptoms, and implications. In this blog, we’ll delve into the key differences between herpes zoster and herpes simplex to provide clarity on these often-confused conditions.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Herpes Zoster?
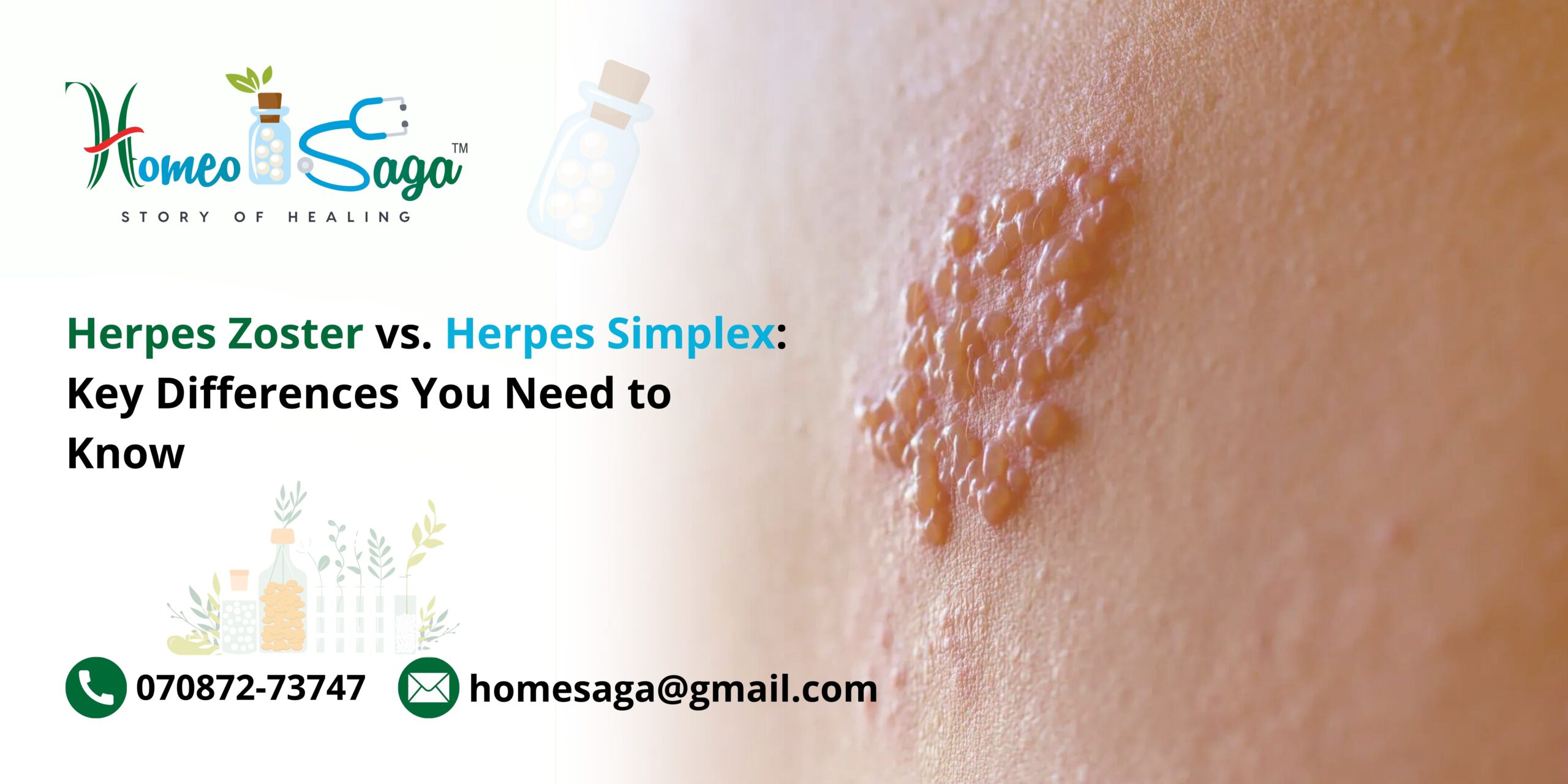
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles, arises from the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). This is the same virus that causes chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate later, particularly in older adults or those with weakened immune systems.
The most recognizable symptom of herpes zoster is a painful, blistering rash that typically appears on one side of the body, following a dermatomal pattern. This means the rash corresponds to a specific nerve root, affecting a localized area of skin. Additional symptoms can include fever, headache, and fatigue. While the rash usually lasts for a few weeks, some individuals may experience postherpetic neuralgia, a condition characterized by lingering nerve pain.
What is Herpes Simplex?
Herpes simplex viruses are categorized into two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is primarily associated with oral herpes, resulting in cold sores around the mouth, while HSV-2 is more commonly linked to genital herpes. However, both types can infect either location, making it essential to recognize the potential for crossover.
Symptoms of herpes simplex can vary greatly. Many people remain asymptomatic, but when symptoms do occur, they typically manifest as painful blisters or sores at the site of infection. Initial outbreaks may be accompanied by flu-like symptoms, such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. The herpes simplex virus also lies dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate, leading to recurrent outbreaks.
Key Differences: Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex
-
Causative Agent: The primary difference between herpes zoster and herpes simplex is the virus responsible for each. Herpes zoster is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, while herpes simplex stems from either HSV-1 or HSV-2. Understanding this distinction is crucial when considering treatment options.
-
Symptoms: The symptoms of herpes zoster vs. herpes simplex are notably different. Herpes zoster presents as a localized rash in a dermatomal pattern, whereas herpes simplex can cause sores in both oral and genital regions. This difference in symptom presentation is vital for accurate diagnosis.
-
Pain: Pain associated with herpes zoster is often more intense and can precede the rash, primarily due to nerve involvement. In contrast, the pain from herpes simplex is usually localized to the blisters or sores and may not exhibit the same neuropathic characteristics.
-
Recurrence: When discussing herpes zoster and herpes simplex, recurrence rates differ significantly. Herpes simplex often leads to recurrent outbreaks, while herpes zoster generally results in a single episode. Although rare, shingles can reactivate, but this is less common than the frequent recurrences seen with herpes simplex.
-
Age and Risk Factors: Herpes zoster is more prevalent in older adults, particularly those over 50, and in individuals with compromised immune systems. Herpes simplex, on the other hand, can affect people of all ages, often manifesting first in childhood or early adulthood.
-
Vaccination: An important consideration in the herpes zoster vs. herpes simplex discussion is vaccination. A vaccine is available for herpes zoster, significantly reducing the risk of developing shingles. Currently, no vaccine exists for herpes simplex, but antiviral medications can manage outbreaks effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the differences between herpes zoster and herpes simplex is essential for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Both conditions can have profound impacts on an individual’s quality of life, but recognizing their unique characteristics can lead to better management. If you suspect you have either condition, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate care. By familiarizing yourself with herpes zoster vs. herpes simplex, you empower yourself to navigate the complexities of these viral infections with greater confidence.