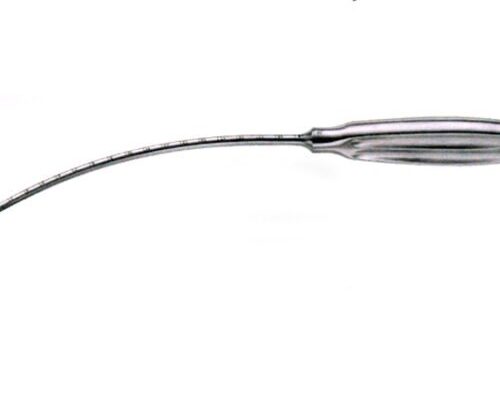
Introduction to the Raspator
A raspator is a specialized surgical instrument used primarily for scraping, cutting, and separating soft tissues or periosteum from bones during medical procedures. Rasparator is widely utilized in orthopedic, dental, and plastic surgery, playing a crucial role in procedures that require precision and minimal tissue damage. Crafted from high-quality stainless steel, raspators come in various shapes and sizes, allowing surgeons to work efficiently while ensuring patient safety.
Importance of the Raspator in Surgery
In many surgical procedures, preserving soft tissues while gaining proper access to the bone is essential. A raspator helps achieve this by carefully lifting and separating tissues without causing unnecessary trauma. This is particularly important in orthopedic surgeries, where exposure of the bone is necessary for procedures such as fracture repair or joint reconstruction. In dental implantology and maxillofacial surgery, raspators aid in bone preparation, ensuring optimal conditions for implant placement or grafting.
By using a raspator, surgeons can create a clean surgical field, allowing for better visualization and precision. The smooth, controlled movement of the instrument ensures minimal bleeding and reduces the risk of excessive tissue damage, leading to faster healing and improved post-operative outcomes.
Design and Variations of Raspators
Raspators are designed with specific surgical needs in mind. They typically feature a long, slender handle for a comfortable grip and a curved or flat blade for efficient tissue manipulation. The blades may be sharp or blunt, depending on the intended use. Sharp-edged raspators are ideal for cutting through tough connective tissues, while blunt-edged versions are used for gentle tissue separation.
Some raspators are double-ended, providing surgeons with versatility by offering different blade designs on each end. Others have ergonomic handles to enhance control and reduce hand fatigue during lengthy procedures. The size and shape of the instrument vary based on its application, with larger raspators commonly used in orthopedic surgery and smaller, more delicate versions utilized in dental or cosmetic procedures.
Surgical Applications of Raspators
The use of raspators extends across multiple medical fields. In orthopedic surgery, they are essential for procedures involving bone grafting, spinal surgeries, and joint reconstructions. Surgeons use them to carefully lift the periosteum, ensuring a clear working area without damaging the underlying bone structure.
In dental and maxillofacial surgery, raspators play a key role in preparing bone surfaces for implants or grafting. They help in shaping and contouring the bone while maintaining soft tissue integrity. Plastic surgeons also rely on raspators during reconstructive and cosmetic procedures to sculpt and refine bone structures, ensuring precise and aesthetically pleasing results.
Conclusion
Raspators are indispensable tools in surgical procedures requiring precise tissue separation and bone exposure. Their ergonomic design, versatility, and effectiveness make them essential in various medical specialties, from orthopedics to dentistry and plastic surgery. By providing surgeons with control and accuracy, raspators contribute to successful surgical outcomes and improved patient recovery. As surgical techniques continue to advance, these instruments remain a fundamental component of modern medical practice.