Exercising is an essential part of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, but for many people, shortness of breath can be an unexpected challenge. Known as Exertional Dyspnea, this condition is characterized by difficulty breathing during physical activity. While shortness of breath can sometimes be mistaken for a lack of fitness, dyspnea health issues can be more complex and may point to underlying health problems. Whether you’re using Home Fitness Equipment or engaging in outdoor activities, understanding exertional dyspnea is key to managing your workouts and ensuring long-term well-being.
Table of Contents
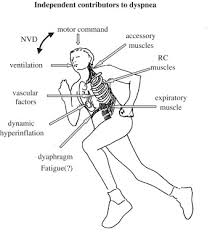
ToggleWhat is Exertional Dyspnea?
Exertional Dyspnea refers to shortness of breath or difficulty breathing that occurs during physical exertion. It is common in both athletes and individuals with underlying health conditions. The sensation can range from mild breathlessness to more severe respiratory discomfort that makes it difficult to continue exercising. For those using Home Fitness Equipment, such as treadmills or stationary bikes, the experience of dyspnea can disrupt workout routines and hinder progress.
While feeling winded during intense exercise is normal, especially for those new to fitness, persistent or sudden onset of dyspnea health issues may indicate a medical condition that requires attention. Cardiovascular diseases, lung conditions like asthma or COPD, and even anxiety can contribute to Exertional Dyspnea.
Causes of Exertional Dyspnea
There are many potential causes for Exertional Dyspnea, ranging from fitness levels to more serious health concerns. Understanding the root cause of shortness of breath is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing further complications.
-
Cardiovascular Issues: Heart-related conditions are one of the most common causes of Exertional Dyspnea. If the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently during exercise, oxygen delivery to the muscles is compromised, leading to shortness of breath. Conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or arrhythmias can cause dyspnea during physical exertion.
-
Lung Problems: Respiratory issues like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pulmonary hypertension can also lead to dyspnea during exercise. In these cases, the lungs struggle to provide enough oxygen to the body, making breathing more difficult.
-
Deconditioning: For individuals who haven’t exercised regularly or have been inactive for a period, Exertional Dyspnea is often a result of deconditioning. When muscles and the cardiovascular system are not accustomed to physical activity, the body becomes less efficient at utilizing oxygen, resulting in shortness of breath.
-
Anxiety: Psychological factors like anxiety or panic attacks can cause breathlessness during exercise. In some cases, people may experience shortness of breath because of anxiety rather than physical exertion itself. Learning to manage mental health during workouts can help alleviate these symptoms.
How Exertional Dyspnea Affects Workouts
For those who regularly use Home Fitness Equipment, such as treadmills, ellipticals, or resistance machines, Exertional Dyspnea can affect workout quality. The feeling of shortness of breath may discourage some individuals from pushing through their exercise routine, resulting in incomplete or suboptimal workouts. This can lead to frustration and may deter people from staying committed to their fitness goals.
Moreover, consistent episodes of dyspnea health issues during workouts may signal an underlying problem that, if left unaddressed, could lead to more serious complications. Individuals experiencing Exertional Dyspnea should be cautious about pushing themselves too hard without understanding the cause of their symptoms. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential for anyone who experiences persistent breathlessness.
Tips for Managing Exertional Dyspnea During Exercise
Dealing with Exertional Dyspnea doesn’t necessarily mean you have to give up on your fitness goals. With the right strategies, it’s possible to manage your symptoms while still staying active.
-
Warm-Up Gradually: A proper warm-up prepares your cardiovascular and respiratory systems for the demands of exercise. Gradually increasing the intensity of your workout gives your body time to adjust and helps reduce the chances of experiencing dyspnea health issues during exercise.
-
Monitor Your Breathing: Being aware of your breathing pattern is crucial when managing Exertional Dyspnea. Focus on slow, deep breaths, particularly when using Home Fitness Equipment. This can help your body maintain better oxygen levels, reducing the sensation of shortness of breath.
-
Start Slowly: For those new to exercising or returning after a long period of inactivity, it’s essential to start with lower-intensity exercises. Walking on a treadmill, cycling on a stationary bike, or using resistance bands can be a good way to begin. As your body adapts, you can gradually increase the intensity of your workouts.
-
Use Interval Training: Interval training, which alternates between short bursts of high-intensity exercise and periods of rest or lower-intensity activity, can be an effective way to build endurance without over-exerting yourself. This technique can help you avoid excessive breathlessness while still challenging your body.
-
Stay Hydrated and Maintain Good Nutrition: Dehydration and poor nutrition can exacerbate dyspnea health symptoms during workouts. Drinking plenty of water and ensuring a balanced diet rich in nutrients supports your cardiovascular and respiratory systems during exercise.
-
Seek Professional Guidance: If your Exertional Dyspnea is severe or persists despite lifestyle modifications, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. A doctor can run diagnostic tests, including lung function tests or cardiac evaluations, to determine the underlying cause of your shortness of breath.
Adapting Your Home Fitness Routine
If you experience Exertional Dyspnea frequently, making adjustments to your Home Fitness Equipment routine can help manage symptoms and improve your fitness over time. Focus on exercises that are low impact but still provide cardiovascular benefits, such as:
- Stationary Biking: Low-impact cycling can help build cardiovascular endurance without putting too much strain on the respiratory system.
- Elliptical Training: This is another excellent low-impact option that allows for a full-body workout without overburdening the lungs.
- Walking on a Treadmill: Walking is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to stay active, and it can be adjusted for any fitness level. You can start with slow-paced walking and gradually increase speed and incline as your endurance improves.
- Resistance Training: Strength training with light weights or resistance bands can be done at home and helps improve muscle tone and overall fitness without overtaxing the respiratory system.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing Exertional Dyspnea is essential for anyone looking to maintain a consistent fitness routine, especially when using Home Fitness Equipment. Shortness of breath can be a barrier to exercise, but it doesn’t have to prevent you from achieving your fitness goals. By recognizing the causes of dyspnea health issues and making necessary adjustments to your workout routine, you can exercise safely and effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen, as underlying health conditions may need to be addressed to ensure your overall well-being.
What the Fuck !
Your Image is not Max Pixels.